Home-based transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) in Alzheimer's disease: rationale and study design, Alzheimer's Research & Therapy
By A Mystery Man Writer
Description
Background Gamma (γ) brain oscillations are dysregulated in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and can be modulated using transcranial alternating stimulation (tACS). In the present paper, we describe the rationale and design of a study assessing safety, feasibility, clinical and biological efficacy, and predictors of outcome of a home-based intervention consisting of γ-tACS over the precuneus. Methods In a first phase, 60 AD patients will be randomized into two arms: ARM1, 8-week precuneus γ-tACS (frequency: 40 Hz, intensity: 2 mA, duration: 5 60-min sessions/week); and ARM2, 8-week sham tACS (same parameters as the real γ-tACS, with the current being discontinued 5 s after the beginning of the stimulation). In a second phase, all participants will receive 8-week γ-tACS (same parameters as the real γ-tACS in the first phase). The study outcomes will be collected at several timepoints throughout the study duration and include information on safety and feasibility, neuropsychological assessment, blood sampling, electroencephalography, transcranial magnetic stimulation neurotransmitter measures, and magnetic resonance imaging or amyloid positron emission tomography. Results We expect that this intervention is safe and feasible and results in the improvement of cognition, entrainment of gamma oscillations, increased functional connectivity, reduction of pathological burden, and increased cholinergic transmission. Conclusions If our expected results are achieved, home-based interventions using γ-tACS, either alone or in combination with other therapies, may become a reality for treating AD. Trial registration PNRR-POC-2022–12376021.
Model-based whole-brain perturbational landscape of neurodegenerative diseases
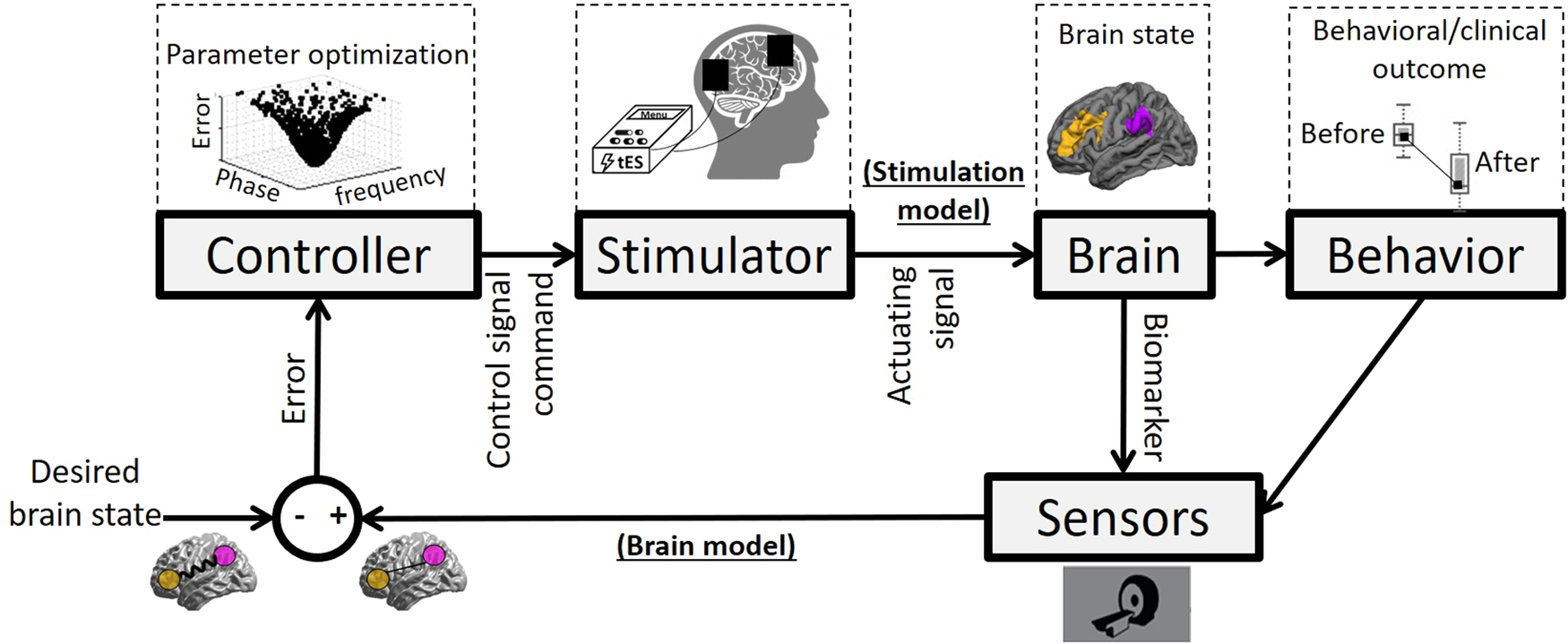
Closing the loop between brain and electrical stimulation: towards precision neuromodulation treatments
Frontiers Tele-supervised home-based transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) for Alzheimer's disease: a pilot study
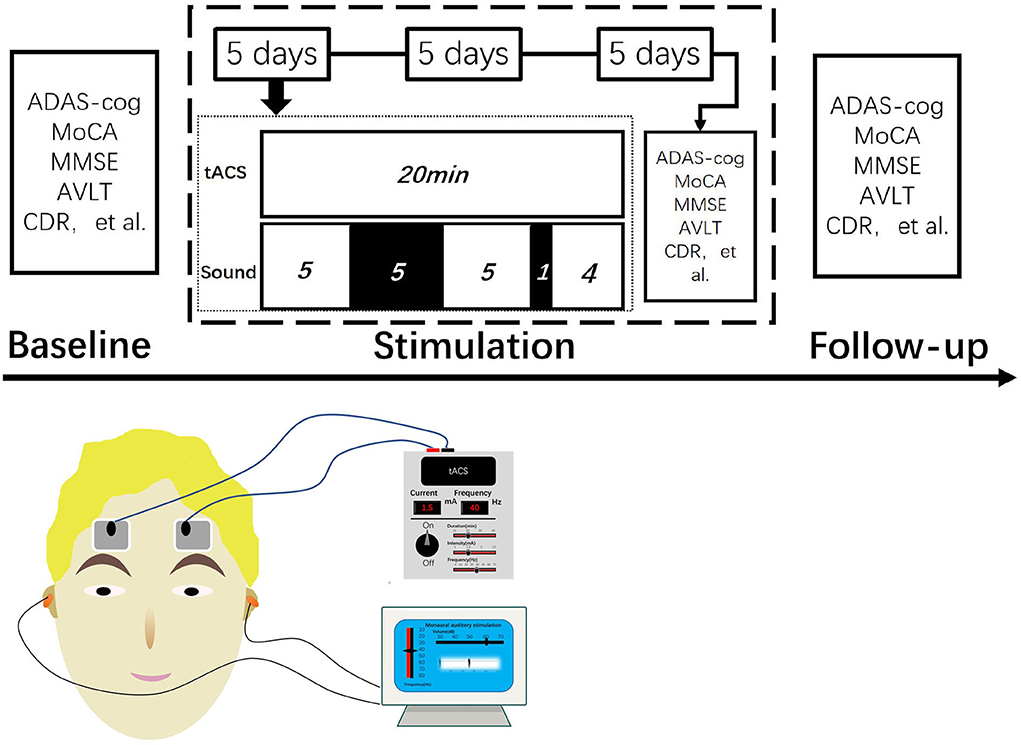
Frontiers Transcranial alternating current stimulation combined with sound stimulation improves the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer's disease: A case report and literature review

Gamma‐induction in frontotemporal dementia (GIFTeD) randomized placebo‐controlled trial: Rationale, noninvasive brain stimulation protocol, and study design - Assogna - 2021 - Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions

Multitracer model for staging cortical amyloid deposition using

Flowchart of study patients. Legend: tACS ¼ transcranial alternating
1x1 tACS Device - Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation – Soterix Medical

Multitracer model for staging cortical amyloid deposition using

In-vivo phase-dependent enhancement and suppression of brain oscillations by transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)

Comparison of online and offline applications of dual-site transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) over the pre-supplementary motor area (preSMA) and right inferior frontal gyrus (rIFG) for improving response inhibition - ScienceDirect
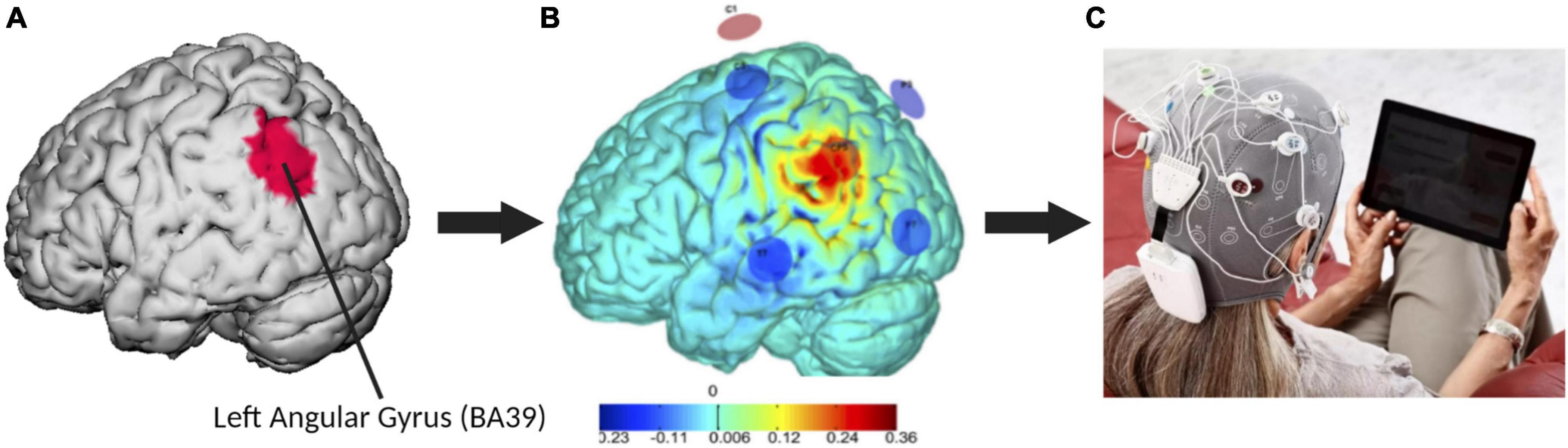
Frontiers Tele-supervised home-based transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) for Alzheimer's disease: a pilot study

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation - an overview
Using gamma-band transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) to improve sleep quality and cognition in patients with mild neurocognitive disorders due to Alzheimer's disease: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial

Toward noninvasive brain stimulation 2.0 in Alzheimer's disease. - Abstract - Europe PMC
from
per adult (price varies by group size)







